「排泄器官」修訂間的差異檢視原始碼討論檢視歷史
(创建页面,内容为“'''排泄器官'''是将机体新陈代谢过程中产生的终产物排出体外的器官。 由于动物进化水平不同和适应多变环境的结果,排泄…”) |
|||
| (未顯示同一使用者於中間所作的 1 次修訂) | |||
| 行 1: | 行 1: | ||
| − | '''排泄器官'''是将机体新陈代谢过程中产生的终产物排出体外的器官。 由于动物进化水平不同和适应多变环境的结果,排泄器官一般可分为下列5类:①原生动物的伸缩泡。②昆虫的马尔皮基氏小管。③甲壳动物的触角腺。④无脊椎动物的肾器官,包括原肾管、后肾管和肾管。⑤脊椎动物的肾脏。 | + | {| class="wikitable" style="float:right; margin: -10px 0px 10px 20px; text-align:left" |
| + | |<center>'''排泄器官'''<br><img src="https://preview.21cnjy.com/files/d4/8c/d48c24d3396283f81abf18e6adafc61a.png" width="280"></center><small>[https://www.21cnjy.com/H/11/41647/9093397.shtml 圖片來自21世纪教育]</small> | ||
| + | |}'''排泄器官'''是将[[ 机体]] 新陈代谢过程中产生的终产物排出体外的[[ 器官]] 。 由于动物进化水平不同和适应多变环境的结果,排泄器官一般可分为下列5类:①原生动物的[[ 伸缩泡]] 。②昆虫的[[ 马尔皮基氏小管]] 。③[[ 甲壳动物]] 的[[ 触角腺]] 。④[[ 无脊椎动物]] 的肾器官,包括[[ 原肾管]] 、[[ 后肾管]] 和[[ 肾管]] 。⑤[[ 脊椎动物]] 的肾脏。 | ||
==脊椎动物== | ==脊椎动物== | ||
| − | 脊椎动物在胚胎时期都有前肾出现,但只有鱼类和两栖类的胚胎时期,前肾才有作用。圆口纲中的盲鳗仍用此种肾脏作为排泄器官。 | + | 脊椎动物在[[ 胚胎时期]] 都有[[ 前肾]] 出现,但只有鱼类和两栖类的胚胎时期,前肾才有作用。圆口纲中的盲鳗仍用此种肾脏作为排泄[[ 器官]] 。 |
===前肾=== | ===前肾=== | ||
前肾的位置靠近体腔的前段,由许多排泄小管(肾小管renal tubules)组成。小管的一端开口于体腔,开口处膨大成漏斗状,其上着生纤毛,这就是肾口,可以直接从体腔内收集代谢废物。在肾口附近还有由血管丛形成的血管球,它们利用滤过血液的方式把血中的废物排出送入排泄小管中。小管的另一端与一个总的管道相通。这个总管称为前肾导管,其末端通到体外。 | 前肾的位置靠近体腔的前段,由许多排泄小管(肾小管renal tubules)组成。小管的一端开口于体腔,开口处膨大成漏斗状,其上着生纤毛,这就是肾口,可以直接从体腔内收集代谢废物。在肾口附近还有由血管丛形成的血管球,它们利用滤过血液的方式把血中的废物排出送入排泄小管中。小管的另一端与一个总的管道相通。这个总管称为前肾导管,其末端通到体外。 | ||
| 行 15: | 行 17: | ||
排泄作用是指生物体将代谢废物排出体外的作用,是所有生物生存的必要过程。单细胞生物透过细胞表面排出废物。高级植物以叶面上的气孔排气。多细胞生物则有特别的排泄器官。其中有参与排泄作用的器官(其他系统的一部分),也可归类到排泄系统(Excretory system)的一部分。 | 排泄作用是指生物体将代谢废物排出体外的作用,是所有生物生存的必要过程。单细胞生物透过细胞表面排出废物。高级植物以叶面上的气孔排气。多细胞生物则有特别的排泄器官。其中有参与排泄作用的器官(其他系统的一部分),也可归类到排泄系统(Excretory system)的一部分。 | ||
==无脊椎动物== | ==无脊椎动物== | ||
| − | (一)无特殊排泄器.如腔肠动物等,由各个细胞直接进行气体交换和排出废物;棘皮动物由体腔液中的变形细胞收集代谢产物,穿过皮鳃逸出体外。 | + | (一)无特殊排泄器.如[[ 腔肠动物]] 等,由各个[[ 细胞]] 直接进行气体交换和排出废物;棘皮动物由体腔液中的变形细胞收集代谢产物,穿过皮鳃逸出体外。 |
| − | (二)收缩泡.见于淡水产原生动物及多孔动物. | + | (二)[[ 收缩泡]].见于淡水产原生动物及多孔动物. |
| − | (三)原肾型.见于扁形动物、有假体腔的动物及环节动物和软体动物的幼虫.基本构造为1对纵行的排泄管及数目不等的焰细胞,焰细胞中空,内有1束不断摆动的纤毛,把收集的废物送至排泄管,由排泄孔排出.但线虫类只有1个由原肾细胞衍生的管状或H状细胞,细胞内无纤毛,排泄管为细胞内管道. | + | (三)[[ 原肾]] 型.见于扁形动物、有假体腔的动物及[[ 环节动物]] 和[[ 软体动物]] 的幼虫.基本构造为1对纵行的排泄管及数目不等的焰细胞,焰细胞中空,内有1束不断摆动的纤毛,把收集的废物送至排泄管,由排泄孔排出.但线虫类只有1个由原肾细胞衍生的管状或H状细胞,细胞内无纤毛,排泄管为细胞内管道. |
| − | (四)后肾型.见于环节动物和软体动物.基本构造包括开口于体腔的1对或多对腺状器官,由肾孔排出代谢废物.环节动物的后肾管(外胚层来源)可和中胚层来源的体腔导管合成共同的管道及排泄孔.有的种类也可由原肾管与体腔导管合成.有些甲壳纲动物具有类似后肾管的排泄器,称触角腺. | + | (四)后肾型.见于环节动物和软体动物.基本构造包括开口于体腔的1对或多对腺状器官,由肾孔排出代谢废物.环节动物的后肾管(外胚层来源)可和中胚层来源的体腔导管合成共同的管道及排泄孔.有的种类也可由原肾管与体腔导管合成.有些甲壳纲动物具有类似后肾管的排泄器,称[[ 触角腺. |
| − | (五)马氏管.见于陆栖的节肢动物.马氏管呈丝状,自2条至数百条,浸于血液中.马氏管的管壁只有1层细胞,末端为盲端,另一端通入肠道,代谢废物由肛门排出体外. | + | (五)[[ 马氏管]].见于陆栖的[[ 节肢动物]].马氏管呈丝状,自2条至数百条,浸于血液中.马氏管的管壁只有1层[[ 细胞]] ,末端为盲端,另一端通入肠道,代谢废物由肛门排出体外. |
===GOOGLE=== | ===GOOGLE=== | ||
英文翻译:Invertebrates to rid the body of waste organs. The general sub-situations: (1) no special drainage devices. Such as coelenterate, etc. directly from the various cells, gas exchange and discharge of waste; echinoderms from the deformation of body cavity fluid cell collection metabolites across the skin gills escape in vitro. (2) contraction bubble. protozoa found in fresh water and porous animal production. (3) of the original kidney. found in Platyhelminthes, there are fake body cavity of animals and part of animals and molluscs larvae. the basic structure for the 1 on the longitudinal excretory duct and the number of lines, ranging from flame cell flame cell hollow, containing a bundle of cilia continue to swing to the collection of waste sent to the excretory duct, excretory pore from the exhaust. But the line of insects is only one original cell-derived renal tubular or H-shaped cells, nonciliated cells, excretory duct cells of pipes for. (4) after the kidney-type. found in annelid and molluscs. the basic structure, including openings in the body cavity of the 1 on one or more pairs of glandular organs, metabolic wastes discharged by the kidneys Kong. annelid post-renal tube (ectodermal origin) and the mesoderm may be the source of the body cavity tube synthesis of the common ducts and excretory pore. Some species can also be the original kidney tube and body cavity catheter synthesis. some crustacean similar excretion of renal tube device, saying antennary gland. (5) Malpighian tubules. found in terrestrial arthropods. Malpighian tubules was filamentous, from two to hundreds of Article immersed in the blood. Malpighian tubules of the wall is only one layer of cells, the end of the blind side, other side of the pass into the gastro-intestinal, metabolic wastes excreted by the anus. | 英文翻译:Invertebrates to rid the body of waste organs. The general sub-situations: (1) no special drainage devices. Such as coelenterate, etc. directly from the various cells, gas exchange and discharge of waste; echinoderms from the deformation of body cavity fluid cell collection metabolites across the skin gills escape in vitro. (2) contraction bubble. protozoa found in fresh water and porous animal production. (3) of the original kidney. found in Platyhelminthes, there are fake body cavity of animals and part of animals and molluscs larvae. the basic structure for the 1 on the longitudinal excretory duct and the number of lines, ranging from flame cell flame cell hollow, containing a bundle of cilia continue to swing to the collection of waste sent to the excretory duct, excretory pore from the exhaust. But the line of insects is only one original cell-derived renal tubular or H-shaped cells, nonciliated cells, excretory duct cells of pipes for. (4) after the kidney-type. found in annelid and molluscs. the basic structure, including openings in the body cavity of the 1 on one or more pairs of glandular organs, metabolic wastes discharged by the kidneys Kong. annelid post-renal tube (ectodermal origin) and the mesoderm may be the source of the body cavity tube synthesis of the common ducts and excretory pore. Some species can also be the original kidney tube and body cavity catheter synthesis. some crustacean similar excretion of renal tube device, saying antennary gland. (5) Malpighian tubules. found in terrestrial arthropods. Malpighian tubules was filamentous, from two to hundreds of Article immersed in the blood. Malpighian tubules of the wall is only one layer of cells, the end of the blind side, other side of the pass into the gastro-intestinal, metabolic wastes excreted by the anus. | ||
==参考文献== | ==参考文献== | ||
於 2023年7月7日 (五) 15:14 的修訂
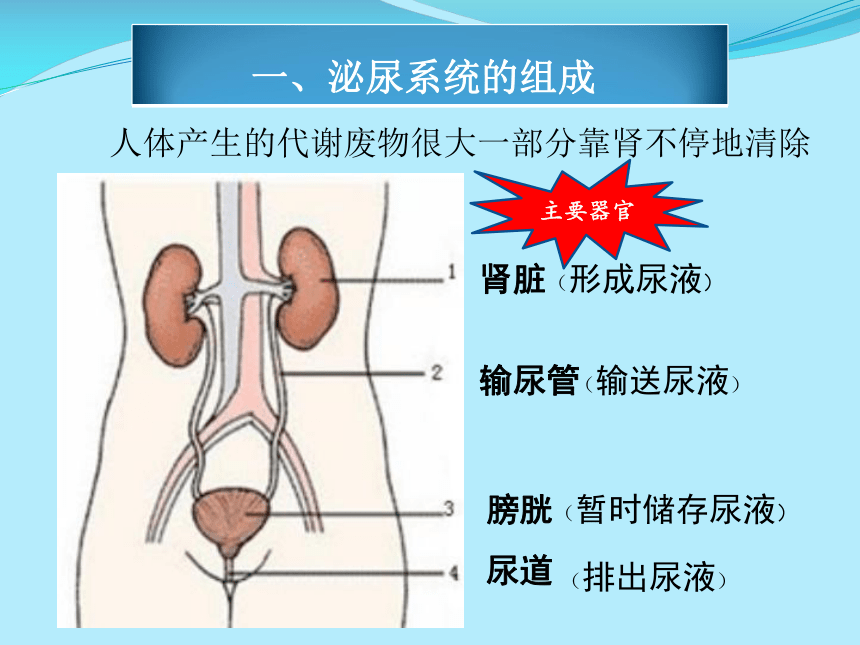 |
排泄器官是將機體新陳代謝過程中產生的終產物排出體外的器官。 由於動物進化水平不同和適應多變環境的結果,排泄器官一般可分為下列5類:①原生動物的伸縮泡。②昆蟲的馬爾皮基氏小管。③甲殼動物的觸角腺。④無脊椎動物的腎器官,包括原腎管、後腎管和腎管。⑤脊椎動物的腎臟。
脊椎動物
脊椎動物在胚胎時期都有前腎出現,但只有魚類和兩棲類的胚胎時期,前腎才有作用。圓口綱中的盲鰻仍用此種腎臟作為排泄器官。
前腎
前腎的位置靠近體腔的前段,由許多排泄小管(腎小管renal tubules)組成。小管的一端開口於體腔,開口處膨大成漏斗狀,其上着生纖毛,這就是腎口,可以直接從體腔內收集代謝廢物。在腎口附近還有由血管叢形成的血管球,它們利用濾過血液的方式把血中的廢物排出送入排泄小管中。小管的另一端與一個總的管道相通。這個總管稱為前腎導管,其末端通到體外。
中腎
中腎是魚類和兩棲類成體階段執行排泄機能的器官,位於前腎的後方。排泄小管的腎口已顯出退化,有些小管的腎口甚至完全退化,不能直接與體腔相通。靠近腎口附近的排泄小管外凸成為小支,小支末端膨大內陷成為雙層的囊狀結構,叫做腎球囊(包曼氏囊),把血管球包入其中,共同形成腎小體(malpighian body)。腎小體和它的排泄小管一起組成一個泌尿機能的基本構造,特稱為腎單位(nephron)。
在中腎階段,原來的前腎導管縱裂為二,其一成為匯集排泄小管尿液的總管道,即中腎導管,在雄性動物兼有輸精管的作用;另一管在雄體已退化,在雌體則演變為輸卵管。
後腎
後腎是爬行類、鳥類、哺乳類成體的排泄器官,其位置靠近體腔的後段。外部形態因動物種類不同而有差別。後腎的排泄小管末端只有腎小體,腎口已完全消失。各腎小管運送尿液匯入的總管道,就是後腎導管(前腎導管,中腎導管和後腎導管,通常亦泛稱為輸尿管)。此管是由中腎導管生出來的一對突起,向前延伸成管,各和一個後腎連接。後腎發生後,中腎和中腎導管都失去了泌尿的機能而轉成生殖系統的組成部分,中腎導管完全成為輸精管,遺留下來的中腎排泄小管則形成副睾等構造。
後腎是脊椎動物腎臟中最高級的類型。就哺乳類而言,它的後腎是一對常呈豆形的主要的排泄器官,濾出尿液,經輸尿管,膀胱和尿道而排出體外。
排泄作用是指生物體將代謝廢物排出體外的作用,是所有生物生存的必要過程。單細胞生物透過細胞表面排出廢物。高級植物以葉面上的氣孔排氣。多細胞生物則有特別的排泄器官。其中有參與排泄作用的器官(其他系統的一部分),也可歸類到排泄系統(Excretory system)的一部分。
無脊椎動物
(一)無特殊排泄器.如腔腸動物等,由各個細胞直接進行氣體交換和排出廢物;棘皮動物由體腔液中的變形細胞收集代謝產物,穿過皮鰓逸出體外。
(二)收縮泡.見於淡水產原生動物及多孔動物.
(三)原腎型.見於扁形動物、有假體腔的動物及環節動物和軟體動物的幼蟲.基本構造為1對縱行的排泄管及數目不等的焰細胞,焰細胞中空,內有1束不斷擺動的纖毛,把收集的廢物送至排泄管,由排泄孔排出.但線蟲類只有1個由原腎細胞衍生的管狀或H狀細胞,細胞內無纖毛,排泄管為細胞內管道.
(四)後腎型.見於環節動物和軟體動物.基本構造包括開口於體腔的1對或多對腺狀器官,由腎孔排出代謝廢物.環節動物的後腎管(外胚層來源)可和中胚層來源的體腔導管合成共同的管道及排泄孔.有的種類也可由原腎管與體腔導管合成.有些甲殼綱動物具有類似後腎管的排泄器,稱[[觸角腺.
(五)馬氏管.見於陸棲的節肢動物.馬氏管呈絲狀,自2條至數百條,浸於血液中.馬氏管的管壁只有1層細胞,末端為盲端,另一端通入腸道,代謝廢物由肛門排出體外.
英文翻譯:Invertebrates to rid the body of waste organs. The general sub-situations: (1) no special drainage devices. Such as coelenterate, etc. directly from the various cells, gas exchange and discharge of waste; echinoderms from the deformation of body cavity fluid cell collection metabolites across the skin gills escape in vitro. (2) contraction bubble. protozoa found in fresh water and porous animal production. (3) of the original kidney. found in Platyhelminthes, there are fake body cavity of animals and part of animals and molluscs larvae. the basic structure for the 1 on the longitudinal excretory duct and the number of lines, ranging from flame cell flame cell hollow, containing a bundle of cilia continue to swing to the collection of waste sent to the excretory duct, excretory pore from the exhaust. But the line of insects is only one original cell-derived renal tubular or H-shaped cells, nonciliated cells, excretory duct cells of pipes for. (4) after the kidney-type. found in annelid and molluscs. the basic structure, including openings in the body cavity of the 1 on one or more pairs of glandular organs, metabolic wastes discharged by the kidneys Kong. annelid post-renal tube (ectodermal origin) and the mesoderm may be the source of the body cavity tube synthesis of the common ducts and excretory pore. Some species can also be the original kidney tube and body cavity catheter synthesis. some crustacean similar excretion of renal tube device, saying antennary gland. (5) Malpighian tubules. found in terrestrial arthropods. Malpighian tubules was filamentous, from two to hundreds of Article immersed in the blood. Malpighian tubules of the wall is only one layer of cells, the end of the blind side, other side of the pass into the gastro-intestinal, metabolic wastes excreted by the anus.